An empty sled of mass 25 kg – Prepare for an exhilarating journey into the world of physics and dynamics as we delve into the captivating topic of an empty sled with a mass of 25 kilograms. This sled, seemingly simple yet brimming with scientific intrigue, offers a unique lens through which we can explore fundamental concepts like mass, energy, and motion.
From its physical characteristics to its potential and kinetic energy, we will embark on an in-depth analysis of this sled, unraveling the forces that govern its behavior. Along the way, we will uncover practical insights into friction and resistance, safety considerations, and even explore innovative design modifications that can enhance its performance.
Physical Characteristics: An Empty Sled Of Mass 25 Kg
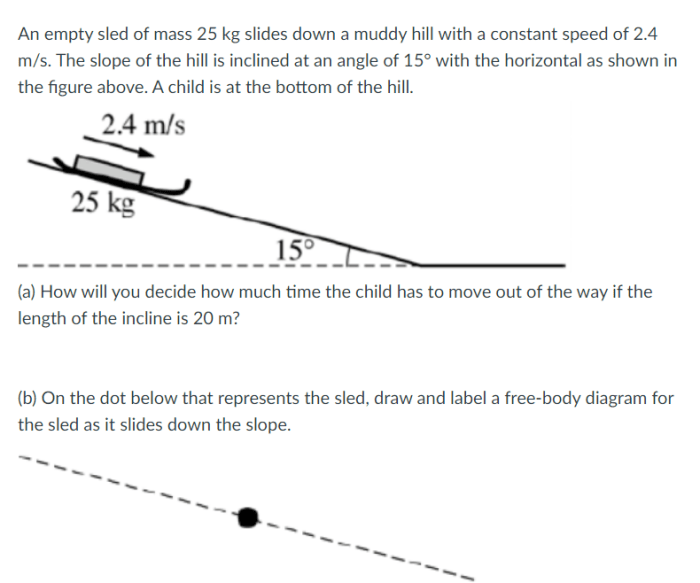
The dimensions of an empty sled with a mass of 25 kg typically vary depending on its intended use and design. However, a common size for a recreational sled used for snow activities is approximately 120 cm in length, 60 cm in width, and 25 cm in height.The
sled is typically constructed using durable materials such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or fiberglass. These materials provide a combination of strength, flexibility, and resistance to wear and tear. The sled’s base is usually reinforced with steel runners to enhance its stability and gliding performance on snow.The
sled may also include additional features such as a molded seat, backrest, and handles for added comfort and control. Some models may have a tow rope or harness for easy pulling or towing behind a snowmobile or other vehicle. The overall weight of the sled, including any accessories, can vary depending on the specific design and materials used.
Mass and Weight
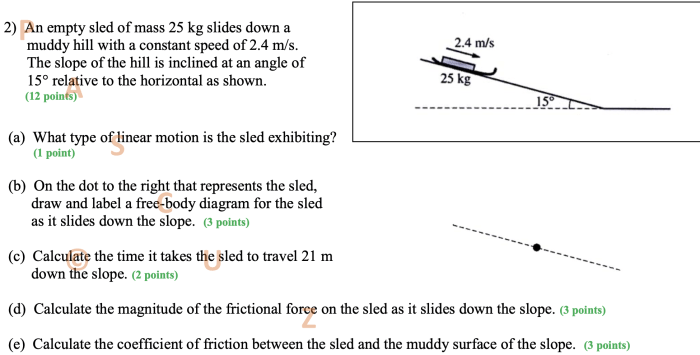
Mass and weight are two distinct physical properties that are often confused. Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, while weight is a measure of the force exerted on an object due to gravity.
The mass of an object is constant, regardless of its location. The weight of an object, however, can vary depending on the strength of the gravitational field it is in. For example, an object that weighs 100 Newtons on Earth would weigh less on the Moon, where the gravitational field is weaker.
Relationship between Mass and Weight
The relationship between mass and weight is given by the following equation:
$$Weight = mass × gravity$$
where:
- Weight is measured in Newtons (N)
- Mass is measured in kilograms (kg)
- Gravity is measured in meters per second squared (m/s^2)
On Earth’s surface, the acceleration due to gravity is approximately 9.8 m/s^2. This means that an object with a mass of 1 kg weighs approximately 9.8 N.
Gravitational Force
The weight of an object is caused by the gravitational force exerted on it by the Earth. Gravitational force is a force that attracts any two objects with mass. The greater the mass of an object, the greater its gravitational force.
The gravitational force between two objects is given by the following equation:
$$F = G × (m_1 × m_2) / r^2$$
where:
- F is the gravitational force in Newtons (N)
- G is the gravitational constant (6.674 × 10^-11 N m^2 / kg^2)
- m_1 and m_2 are the masses of the two objects in kilograms (kg)
- r is the distance between the centers of the two objects in meters (m)
The weight of an object is the gravitational force exerted on it by the Earth. The mass of an object is a measure of the amount of matter in it. The relationship between mass and weight is given by the equation Weight = mass × gravity.
Friction and Resistance

Friction plays a significant role in the motion of a sled. It is the force that opposes the sled’s movement due to contact with the surface it slides on. There are two main types of friction that act on a sled: static friction and kinetic friction.
Static friction acts when the sled is at rest, preventing it from moving. Kinetic friction acts when the sled is in motion, opposing its movement.Friction affects the sled’s motion and speed in several ways. It reduces the sled’s acceleration and speed as it slides down the hill.
The amount of friction depends on the nature of the surface the sled is sliding on. Surfaces with higher coefficients of friction, such as rough or icy surfaces, create more friction and slow the sled down more quickly. Conversely, surfaces with lower coefficients of friction, such as smooth or waxed surfaces, create less friction and allow the sled to slide faster.To
An empty sled of mass 25 kg is sitting on a hill. If we were to search for words that rhyme with envy , we would find plenty of options. After all, the sled is empty, and there are many words that rhyme with “empty.”
But for now, let’s focus on the sled itself.
reduce friction and improve the sled’s performance, several methods can be employed. One common method is to lubricate the surface the sled slides on. Lubricants, such as wax or oil, reduce the coefficient of friction between the sled and the surface, allowing it to slide more easily.
Another method is to use a sled with a streamlined design. Streamlined designs reduce air resistance, which can also slow the sled down.
Design and Modifications
Optimizing the design and making modifications to a sled can significantly enhance its efficiency and functionality. By incorporating different materials, shapes, and features, the sled’s performance can be tailored to specific requirements and conditions.
Materials
- Lightweight Materials:Utilizing materials like aluminum or carbon fiber reduces the sled’s overall weight, enhancing its acceleration and maneuverability.
- Durable Materials:Incorporating materials such as polyethylene or fiberglass ensures the sled’s durability and resistance to wear and tear, extending its lifespan.
- Low-Friction Materials:Employing materials with low coefficients of friction, such as Teflon or ceramic, minimizes resistance and improves the sled’s gliding ability.
Shapes
- Streamlined Shape:A streamlined shape minimizes air resistance and allows the sled to move smoothly through the air.
- Curved Bottom:A curved bottom provides a smooth transition between the sled and the surface it is sliding on, reducing friction.
- Raised Sides:Raised sides prevent snow from accumulating on the sled, maintaining its weight and enhancing its stability.
Features, An empty sled of mass 25 kg
- Steering Mechanism:Incorporating a steering mechanism allows the rider to control the sled’s direction, enhancing maneuverability.
- Braking System:Implementing a braking system provides the rider with control over the sled’s speed and ensures safety.
- Ergonomic Design:Designing the sled with an ergonomic shape and comfortable seating improves the rider’s comfort and control.
Comparison of Sled Designs
| Design | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Sled | Simple and inexpensive; easy to construct | Heavy; limited maneuverability; prone to snow accumulation |
| Plastic Sled | Lightweight; durable; low friction | Less maneuverable; may not be suitable for all snow conditions |
| Inflatable Sled | Lightweight; easy to store; comfortable | Not as durable; can puncture; requires inflation |
| Racing Sled | Streamlined; low friction; high speed | Expensive; requires specialized skills; not suitable for all terrains |
Safety Considerations

Sledding is a fun and exciting winter activity, but it can also be dangerous if proper safety precautions are not taken. Here are some potential hazards to be aware of and guidelines for safe sledding practices.
Potential Hazards
- Collisions:Sleds can travel at high speeds, and collisions with other sleds, trees, or obstacles can cause serious injuries.
- Falls:Sleds can tip over or go out of control, causing riders to fall and hit the ground.
- Frostbite and hypothermia:Sledding can take place in cold weather, and prolonged exposure to the elements can lead to frostbite or hypothermia.
- Drowning:Sledding near bodies of water can be dangerous, as sleds can slide into the water and riders can become trapped.
Safe Sledding Practices
To ensure a safe sledding experience, follow these guidelines:
- Choose a safe sledding hill.The hill should be free of obstacles, trees, and other hazards. It should also have a gradual slope.
- Wear proper protective gear.This includes a helmet, gloves, and warm clothing. A helmet can protect your head from injury in the event of a fall.
- Be aware of your surroundings.Be aware of other sledders, obstacles, and potential hazards.
- Sled with a friend.Having someone to sled with can help you stay safe and can provide assistance if needed.
- Take breaks.Sledding can be tiring, so take breaks to rest and warm up.
- Supervise children.Children should always be supervised by an adult when sledding.
Helpful Answers
What is the significance of the sled’s mass being 25 kg?
The specific mass of 25 kg is not particularly significant in itself. It simply serves as a numerical value to illustrate the concepts and principles being discussed in relation to the sled.
How does the sled’s design affect its performance?
The sled’s design can significantly impact its performance. Factors such as the shape, materials used, and presence of features like runners or brakes can influence its speed, stability, and maneuverability.
Is it safe to sled on all types of hills?
No, it is not safe to sled on all types of hills. It is important to assess the hill’s steepness, visibility, and potential obstacles before sledding. Always prioritize safety and choose hills that are appropriate for your skill level and the sled’s capabilities.