Embark on an enlightening journey with our comprehensive moles molecules and grams worksheet, meticulously crafted to empower you with a profound understanding of these fundamental chemical concepts. Delve into the intricacies of moles as units of measurement, explore the relationship between moles and particles, and unravel the significance of molecular mass, formula mass, molar mass, and concentration in the realm of chemistry.
As you navigate through this interactive worksheet, you will uncover the practical applications of these concepts in diverse fields, ranging from medicine to environmental science. Prepare to be captivated by real-world examples that showcase how moles, molecules, and grams play a pivotal role in solving problems and making informed decisions.
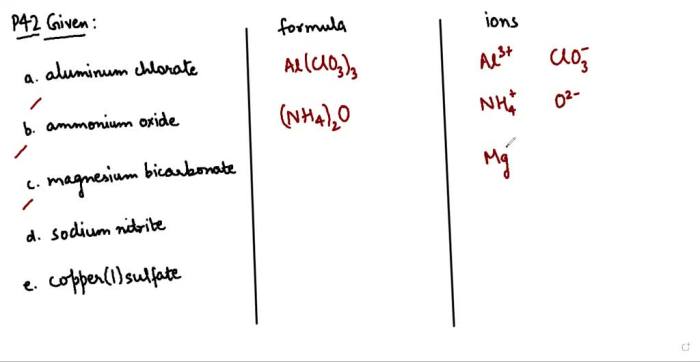
Mole Concepts
A mole is a unit of measurement used to quantify a specific number of particles, such as atoms, molecules, ions, or electrons. It is defined as the amount of substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 0.012 kilograms of carbon-12.
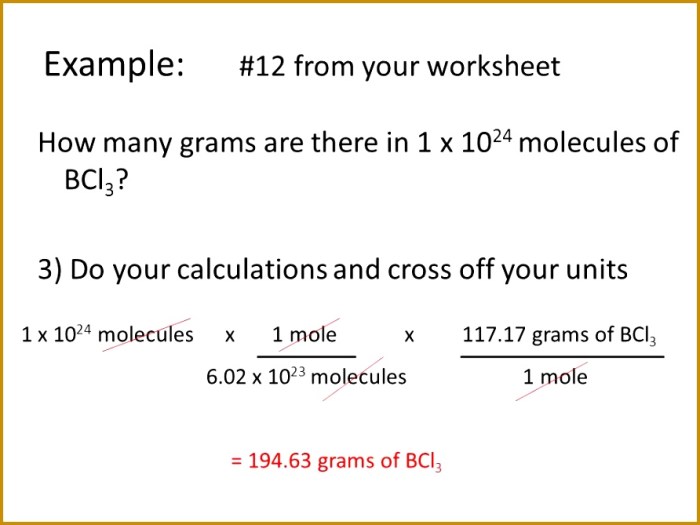
This number is known as Avogadro’s number, which is approximately 6.022 x 10 23.
The mole concept provides a convenient way to express the amount of a substance in terms of the number of particles it contains. For example, 1 mole of water (H 2O) contains 6.022 x 10 23molecules of water.
Relationship between Moles and the Number of Particles
The relationship between moles and the number of particles is given by the following equation:
Number of particles = Number of moles x Avogadro’s number
This equation can be used to convert between the number of moles and the number of particles in a substance.
Examples of How Moles are Used in Chemistry
- To calculate the molar mass of a compound
- To determine the concentration of a solution
- To balance chemical equations
- To perform stoichiometric calculations
Molecular Mass and Formula Mass: Moles Molecules And Grams Worksheet
Definition of Molecular Mass and Formula Mass
Molecular mass is the mass of a single molecule of a compound. It is expressed in atomic mass units (amu) and is calculated by adding the atomic masses of all the atoms in the molecule.
Formula mass is the mass of a formula unit of a compound. It is also expressed in amu and is calculated by adding the atomic masses of all the atoms in the formula unit.
How to Calculate the Molecular Mass and Formula Mass of a Compound
To calculate the molecular mass or formula mass of a compound, follow these steps:
- Identify the elements present in the compound.
- Look up the atomic mass of each element in the periodic table.
- Multiply the atomic mass of each element by the number of atoms of that element in the molecule or formula unit.
- Add the products from step 3 to obtain the molecular mass or formula mass.
Examples of How Molecular Mass and Formula Mass are Used in Chemistry
- To determine the empirical formula of a compound
- To calculate the molar mass of a compound
- To perform stoichiometric calculations
Molar Mass and Concentration
Definition of Molar Mass and Concentration
Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance. It is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol) and is calculated by dividing the mass of the substance by the number of moles of the substance.
Concentration is a measure of the amount of solute present in a given volume of solution. It is expressed in moles per liter (mol/L) and is calculated by dividing the number of moles of solute by the volume of the solution in liters.
How to Calculate the Molar Mass and Concentration of a Solution
To calculate the molar mass or concentration of a solution, follow these steps:
- For molar mass: Divide the mass of the substance by the number of moles of the substance.
- For concentration: Divide the number of moles of solute by the volume of the solution in liters.
Examples of How Molar Mass and Concentration are Used in Chemistry
- To prepare solutions of a known concentration
- To perform stoichiometric calculations
- To determine the identity of an unknown substance
Stoichiometry
Definition of Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is the study of the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. It is used to predict the amount of reactants and products that are involved in a given reaction.
How to Use Stoichiometry to Balance Chemical Equations
To balance a chemical equation using stoichiometry, follow these steps:
- Write the unbalanced chemical equation.
- Identify the atoms that are not balanced.
- Adjust the coefficients in front of the reactants and products to balance the number of atoms of each element.
Examples of How Stoichiometry is Used in Chemistry
- To predict the products of a chemical reaction
- To calculate the amount of reactants or products that are needed or produced in a reaction
- To determine the limiting reactant in a reaction
Applications of Moles, Molecules, and Grams
Applications in Medicine
- To calculate the dosage of a drug
- To determine the concentration of a drug in the blood
- To design new drugs
Applications in Environmental Science
- To monitor the levels of pollutants in the environment
- To assess the impact of pollution on human health
- To develop strategies to reduce pollution
Applications in Materials Science, Moles molecules and grams worksheet
- To design new materials with specific properties
- To improve the performance of existing materials
- To develop new technologies
FAQ Corner
What is the significance of moles in chemistry?
Moles serve as a fundamental unit of measurement in chemistry, representing a specific quantity of particles (atoms, molecules, ions, or electrons). They provide a convenient way to express the amount of a substance involved in a chemical reaction or present in a sample.
How are molecular mass and formula mass calculated?
Molecular mass refers to the mass of a single molecule, while formula mass represents the mass of a compound’s formula unit. To calculate molecular mass, sum the atomic masses of all atoms in the molecule. For formula mass, consider the atomic masses of all atoms present in the empirical formula of the compound.
What is the relationship between molar mass and concentration?
Molar mass, expressed in grams per mole, represents the mass of one mole of a substance. Concentration, often measured in moles per liter (M), indicates the amount of substance dissolved in a specific volume of solution. Molar mass plays a crucial role in determining the concentration of a solution.